VASP-Based High-Throughput First-Principles Calculation Integrated Interface Program
Introduction
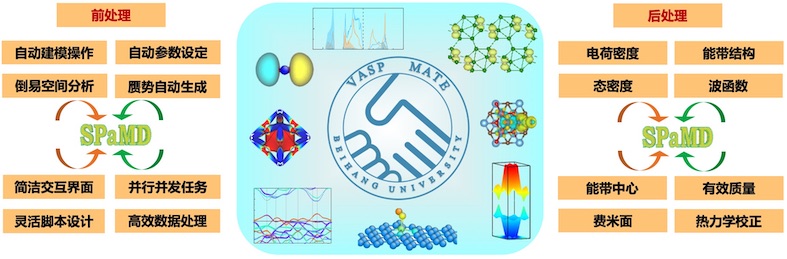
VASPMATE is a powerful and user-friendly command-line tool designed to provide pre- and post-processing support for VASP calculations. The software includes robust preprocessing capabilities for structure modeling and calculation parameter setup, as well as post-processing analysis functions for extracting electronic, energetic, and other physicochemical properties.
The software adopts a concise command mode, making it easy to build robust high-throughput workflow scripts. It has been integrated into the SPaMD platform, supporting user-friendly graphical interface design that can customize complex workflows to automatically derive various first-principles calculation properties. Written in C/C++, it can be compiled and run on Linux, Mac, and Windows systems, featuring compactness, portability, and ease of operation.
Preprocessing Functions
Supercell construction, equivalent cell redefinition, coordinate system conversion, atomic coordinate modification and fixation, supercell deformation, as well as k-point, essential parameter, and pseudopotential setup.
Post-processing Functions
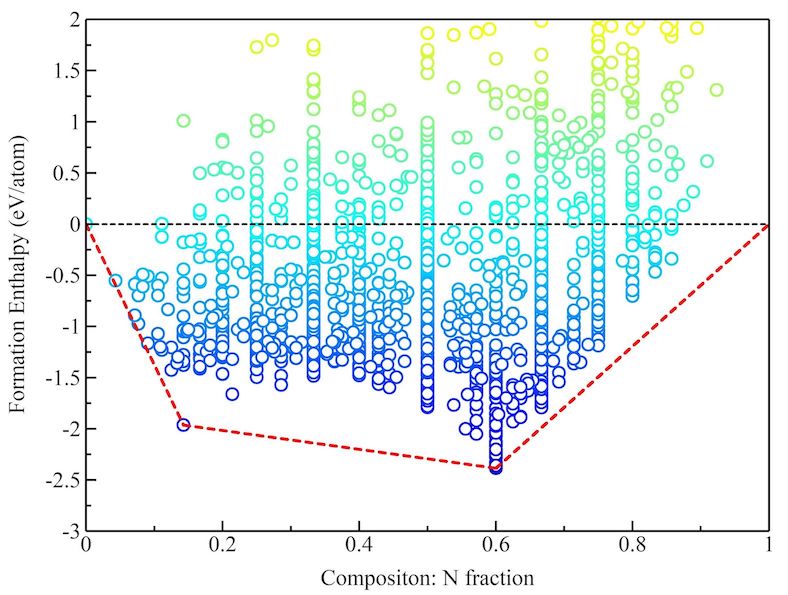
Basic electronic and thermodynamic property analysis, including Kohn-Sham orbitals, band structure, density of states, charge density difference, Fermi surface, thermodynamic energy correction, cohesive energy, formation enthalpy, elastic properties, and SQL database, among others.
Features
- Customize INCAR files based on default templates
- Directly modify control parameters in INCAR files
- Convert POSCAR files from cif format (no fractional occupancy)
- Geometric operations on structures including redefinition, rotation, affine transformation, aliasing, etc.
- Symmetry operations on structures including primitive cell, conventional cell, IEEE standardization, etc.
- Generate KPOINTS files for standard SCF calculations
- Generate k-paths for band structure calculations (PBE or HSE)
- Merge POTCAR based on POSCAR
- Continuous workflow for VASP file generation and validation
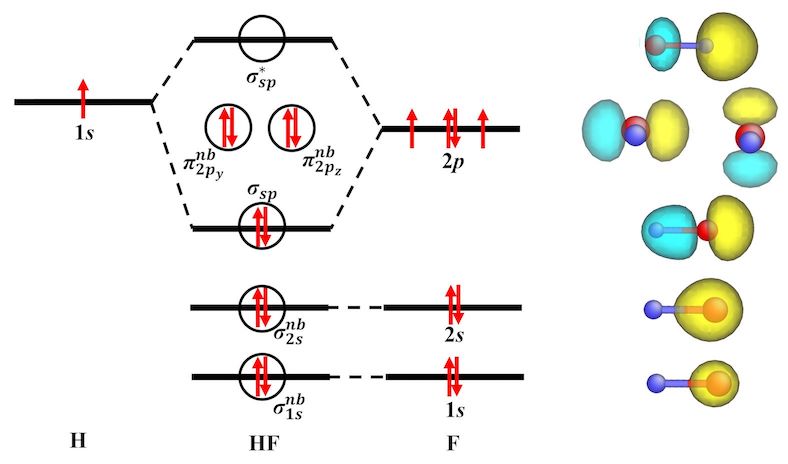
- Wavefunction analysis (e.g., Kohn-Sham orbitals)
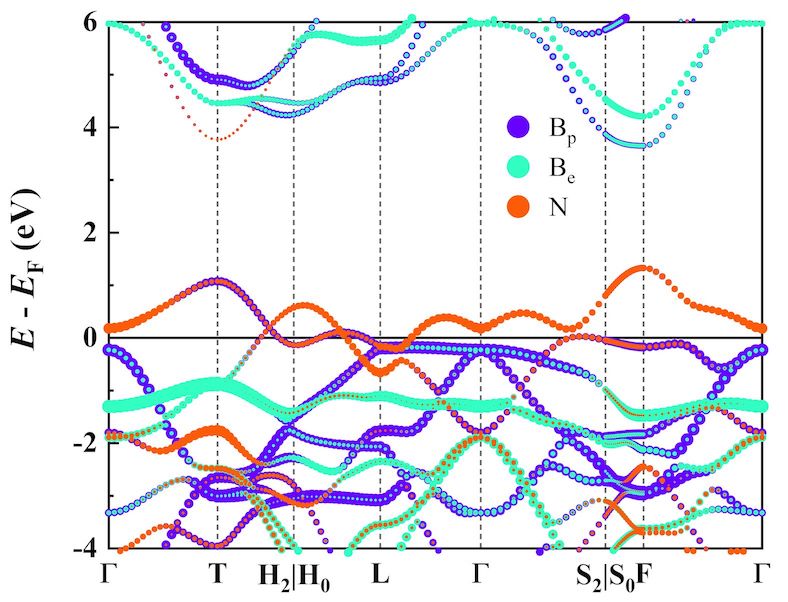
- Basic band structure analysis (PBE)
- Hybrid functional band structure analysis (HSE)
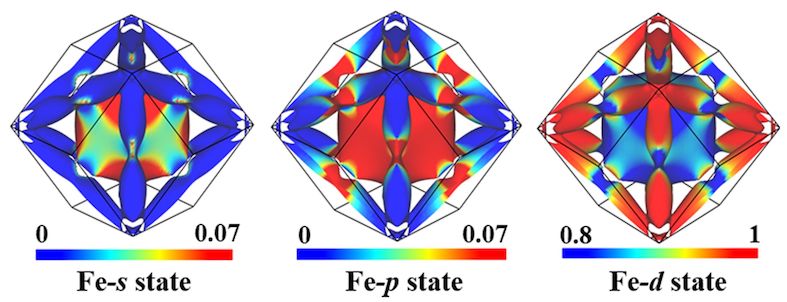
- Density of states analysis
- Band center analysis
- Effective mass analysis
- Fermi surface analysis
- Global 3D band structure analysis
- Charge density difference analysis
- Optical property analysis
- Magnetic property analysis
- Thermodynamic energy correction (gas or adsorbed)
- Formation enthalpy analysis (convex hull method)
- Elastic constant calculation via stress-strain method
- Elastic constant calculation via energy-strain method
- Automatic database construction using sdata, JSON, and SQLite3 formats
- Automatic setup for high-throughput tasks
- Automatic consistency and convergence checking of calculation results
Gallery
VASPMATE Technical Manual


Update History
- Version 2.0: Provides detailed guidebook explaining syntax formats and rules. Adds POSCAR, INCAR, KPOINTS, and POTCAR file operation commands. Enhances automatic setup for high-throughput tasks, adds automatic consistency and convergence checking, supports automatic database construction in sdata/JSON/SQLite3 formats. Adds two elastic constant calculation methods, supports AIMD simulation, random and evolutionary structure generation, etc.
- Version 1.3: Adds optical property analysis and stress-strain method elastic calculation
- Version 1.2: Enhances OUTCAR information extraction functionality
- Version 1.1: Adds electronic pre- and post-analysis functions, including Fermi surface, 3D band structure, Bader charge, and wavefunction analysis, etc.
License Agreement
License Statement: VASPMATE is currently copyrighted and, with our permission, can be freely distributed to academic, scientific, educational, and non-commercial users. Commercial users may also use this software free of charge until a license agreement is established, or through signing a patent authorization or technical support contract. This software is provided "as is" without any express or implied warranties.
Before using VASPMATE, new users please register via the registration link, or send the registration form to email: zrfcms@buaa.edu.cn
Note: Before obtaining VASPMATE sample code, new users please use the registration link, registered users please use the login link
References
Z. C. Pan, Z. R. Liu, T. F. Xu, D. Legut, and R. F. Zhang*. VASPMATE: an integrated
user-interface program
for high-throughput first principles calculation through VASP code, Computational Materials
Science 233,
112707 (2024).
